
Enhance TPU Wear Resistance: Solutions for Wearables, Cable, and Other Finished Products
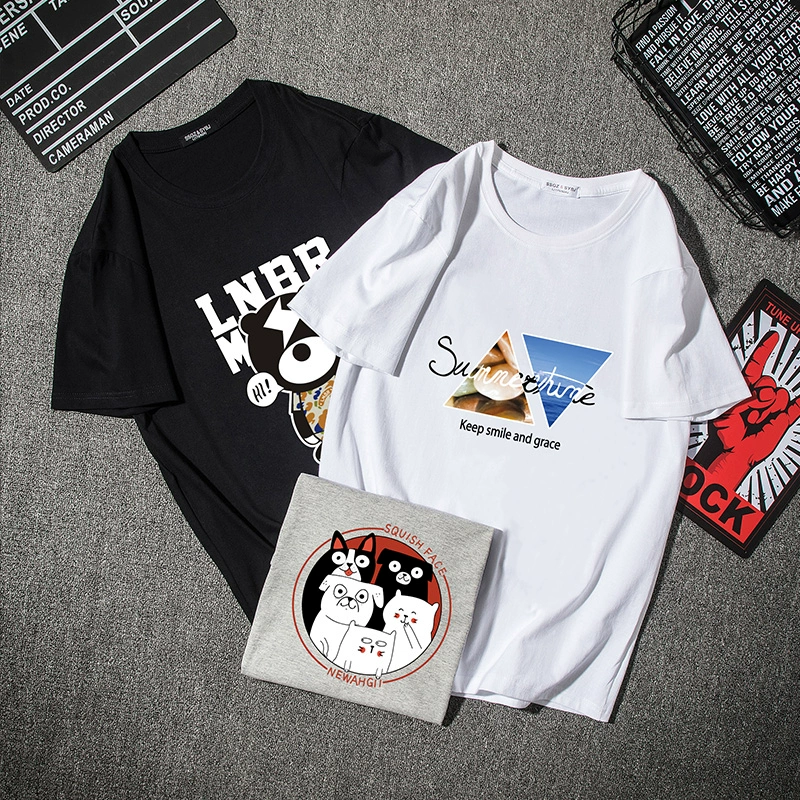
In today’s competitive market, thermoplastic polyurethane (TPU) is widely used in demanding applications such as consumer cable jackets, industrial belts, escalator handrails, wearable device bands, and other high‑flex components. These use cases require not only strong mechanical and elastic properties but also exceptional abrasion resistance and, in many cases, a defined coefficient of friction.
Yet many OEMs and compounders find that even premium TPUs can suffer from surface damage, frictional wear, stick–slip behavior, or premature failure under cyclic bending conditions.
For engineers and design teams, the key question becomes: how can we enhance TPU’s durability without compromising softness, visual finish, or processability?
Traditional Solutions and Their Limitations
Over the years, compounders have tackled TPU wear issues via three main routes:
• Lubricating or anti‑friction additives — e.g., PTFE, molybdenum disulfide, or wax-based systems that reduce surface friction but may migrate or affect surface feel.
• Hard wear-resistant fillers — e.g., ceramic particles or glass beads, which can improve abrasion resistance but often increase hardness or reduce flexibility.
• Micro-crosslinking or reactive systems — aiming to lock in the structure and resist surface deformation, but often impairing recyclability or complicating injection/overmolding processing.
Each of these approaches has trade-offs, including migration over time, surface blooming, loss of softness, reduction of aesthetic/skin-touch finish, or processing complications. As applications increasingly move into wearables, cables, and high-flex thin profiles, there is growing demand for a modifier that maintains flexibility, surface quality, and long-term wear performance.
Introducing Novel and Efficient Wear-Resistant Approaches for TPU Compounders
Recent advances in dynamic vulcanized thermoplastic silicone-based elastomers (Si‑TPV) provide a permanent solution for TPU wear resistance, overcoming the limitations of traditional methods.
This silicone-based Thermoplastic Elastomer is made by a special compatible technology to help silicone rubber be dispersed in TPU evenly as 1~3 micron particles under a microscope. This unique material combines the strength, toughness, and abrasion resistance of any thermoplastic elastomer with desirable properties of silicone: softness, silky feel, UV light, and chemical resistance, which can be recycled and reused in traditional manufacturing processes.
By adding an appropriate amount of Si‑TPV modifier 3100-55A to thermoplastic polyurethane (TPU) elastomers, compounders can achieve enhanced abrasion resistance, improved mechanical stability under cyclic stress, and a long-term soft-touch, skin-friendly tactile finish with a matte effect—all without the drawbacks commonly associated with lubricants, hard fillers, or crosslinking systems, such as migration over time, surface blooming, loss of softness, or reduction of aesthetic and skin-touch properties.
According to customer feedback, internal testing shows a wear-loss reduction of approximately 30–75% and an abrasion resistance improvement of 2–3× compared with standard TPU compounds under company test conditions—far exceeding the performance of conventional wear-resistant TPUs on the market.


How Si‑TPV Imparts Permanent Wear Resistance to TPU?
Key Mechanisms by Which Si‑TPV Surface Modification Enhances TPU Durability and Tactile Performance
Using special compatibilization technology and dynamic vulcanization, silicone rubber particles (1–3 μm) are uniformly dispersed within the TPU matrix, forming a unique “sea-island” morphology. These micron-sized particles create micro-protrusions across the TPU surface, producing a silky, smooth, and skin-friendly tactile feel.
This structure combines the mechanical strength and flexibility of TPU with the premium tactile properties of silicone rubber, while ensuring the silicone particles remain uniformly and stably distributed within the matrix.
The vulcanized silicone rubber particles are inherently soft, acting as the soft segments of the thermoplastic elastomer, which reduces TPU hardness. This eliminates the need for external plasticizers, preventing oil migration issues at the source and supporting long-term surface integrity while resisting surface stickiness.
Si‑TPV contains a high proportion of crosslinked silicone rubber with low surface energy, which reduces the coefficient of friction and abrasion of the composite material.
Because the crosslinked silicone rubber is immobile within the TPU matrix at room temperature, the resulting wear resistance is permanent and consistent, both internally and externally.
Unlike migrating lubricants such as linear siloxanes or waxes, which lose effectiveness once their lubricating layer wears off, Si‑TPV provides lasting wear resistance.
Practical Implementation Tips: Blend the Si‑TPV into your base TPU at a controlled dosage (e.g., 5–10 wt% typical starting point). Maintain processing conditions similar to your TPU system to ensure good dispersion.
If you are a compounder or OEM facing TPU wear challenges—such as cable flex fatigue, surface abrasion & stickiness in Wearables, or high-flex thin-wall applications—Long-Term Silky Skin-Friendly Comfort Soft Touch Material Si‑TPV can help you:
• Impart permanent wear resistance
• Preserve a soft, skin-friendly tactile finish with a matte effect
• Easy processability
Discover how environmentally friendly thermoplastic elastomers Si‑TPV can elevate the durability and performance of your TPU products.
Reach out via amy.wang@silike.cn or visit www.si-tpv.com to explore how to integrate Si‑TPV into your formulations today.








































3.jpg)






